The Longhorn Beetle: Guardians of Biodiversity and Indicators of Change
The world of insects is vast and frequently overlooked, yet it plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. Among the myriad of insect species, the Longhorn Beetle (family: Cerambycidae) stands out with its unique appearance and significant ecological impact. This article delves deep into the fascinating world of Longhorn Beetles, exploring their biology, ecological significance, cultural representation, and the challenges they face in a changing world.
Introduction to Longhorn Beetles
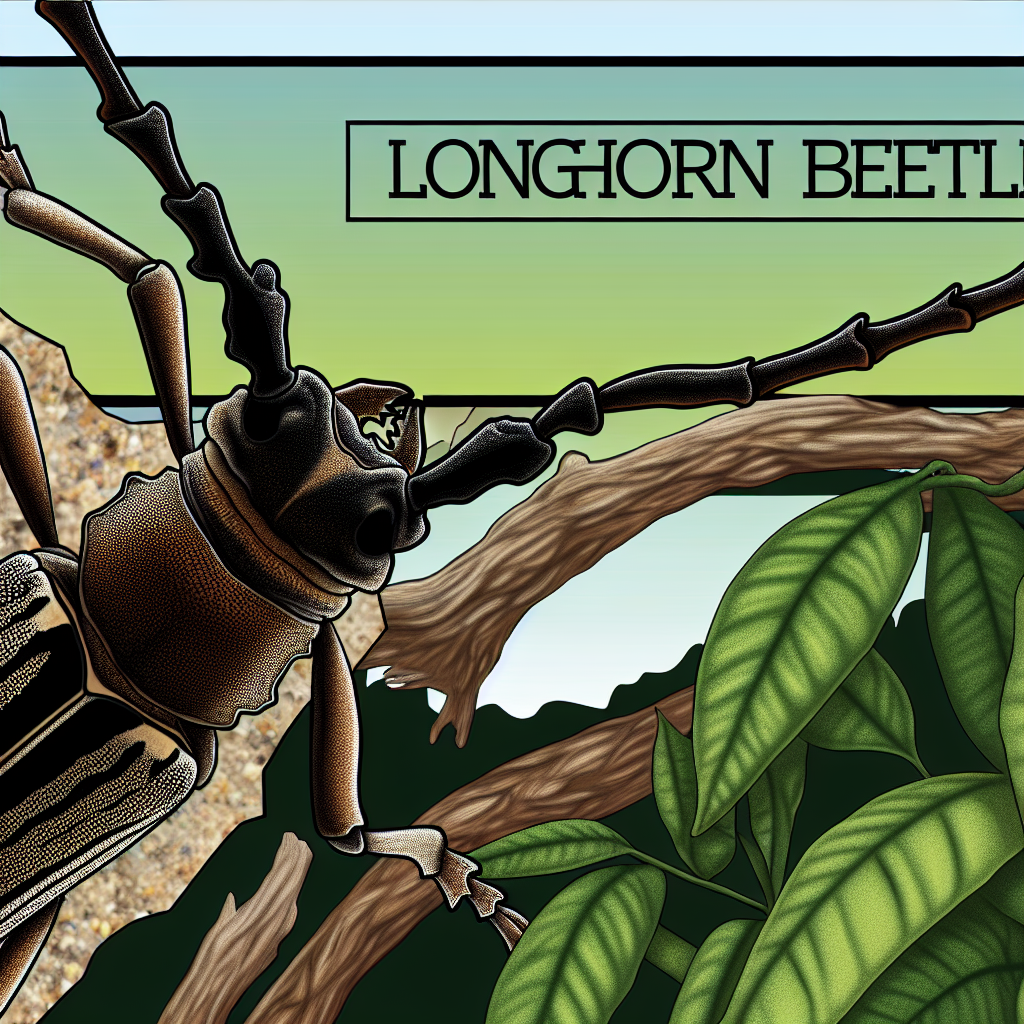
Longhorn Beetles are named for their characteristically long antennae, often surpassing their body length. This diverse family consists of about 35,000 species globally, spread across varied ecosystems—from dense tropical rainforests to more temperate climates. Their sizes differ incredibly, ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters, with some species like the Titanus giganteus, boasting a length of up to 17 centimeters, making it one of the largest beetles in the world.
Anatomy and Identification
Understanding the anatomy of Longhorn Beetles is crucial for their identification and study:
- Antennae: Often as long as or longer than their body, these serve as sensory tools, aiding in navigation and environment detection.
- Body Structure: Comprising the head, thorax, and abdomen. Many species exhibit vibrant colors and elaborate patterns which can serve as camouflage or warning signals to predators.
- Legs and Wings: Equipped with strong legs for gripping bark and leaves; their two pairs of wings are vital for mobility, though some species are flightless.
Lifecycle and Behavior
Longhorn Beetles undergo a complete metamorphosis comprising four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
- Eggs: Laid in crevices on bark or in wood, often preferring dead or decaying trees, which serve as a food source for the larvae.
- Larvae: Known as wood-borers, larvae tunnel through wood, which can lead to structural damage in living trees, but is essential for breaking down and recycling dead wood into soil.
- Pupae and Adult: After pupation within the wood, adults emerge, often in spring or summer, to continue the cycle through mating.
Ecological Role
Longhorn Beetles play a pivotal role in ecosystems:
- Decomposition and Recycling: By breaking down dead wood, they contribute to nutrient cycling in forests, enhancing soil fertility.
- Prey and Predator Dynamics: Serve as food for various birds, mammals, and other insects, anchoring the food web.
- Pollination and Biodiversity: Some species, while feeding on nectar, assist in pollination, indirectly supporting plant diversity.
Cultural and Economic Impact
Culturally, Longhorn Beetles have inspired art and folklore across various communities. However, their interaction with human activities poses significant economic considerations:
- Forestry Impact: While key to natural forests, some species become pests in timber industries, causing economic losses.
- Invasives and Control: Global trade has led to the spread of invasive species like the Asian Longhorn Beetle (Anoplophora glabripennis), necessitating stringent control measures to protect local ecosystems.
Conservation and Challenges
With habitat loss and climate change, Longhorn Beetles face significant challenges:
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation and urbanization threaten their natural habitats, leading to species decline.
- Climate Change: Alterations in temperature and moisture levels affect their life cycles and geographical distribution.
- Conservation Efforts: There is a growing need for informed conservation strategies, focusing on habitat preservation and sustainable forestry practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What do Longhorn Beetles eat?
- Adult Longhorn Beetles primarily feed on nectar, fruit, and young plant tissue, while larvae feed on wood and plant material, playing an essential role in decomposition.
-
Are Longhorn Beetles dangerous?
- While they pose no direct threat to humans, certain species can be destructive to trees and wooden structures due to their larval feeding habits.
-
How can you identify different species of Longhorn Beetles?
- Identification involves examining body size, color patterns, and particularly the length and segmentation of their antennae. Field guides and consultation with entomologists are often employed to differentiate species.
-
What is the largest Longhorn Beetle species?
- The Titanus giganteus, found in the rainforests of South America, holds this title, with some specimens measuring up to 17 centimeters in length.
-
Where are Longhorn Beetles most commonly found?
- They are widespread, with the highest diversity in tropical regions. However, they can be found in various habitats including temperate and even arid environments.
- How do Longhorn Beetles contribute to biodiversity?
- By aiding in wood decomposition and serving as prey for other species, they contribute significantly to ecosystem biodiversity and health.
Longhorn Beetles, with their diverse forms and ecological roles, epitomize the complexity and interconnectivity of life. As we advance in our understanding of their biology and ecological contributions, it is crucial to balance human activities with the conservation of these intricate and essential creatures. Through continued research and awareness, Longhorn Beetles can continue to thrive, ensuring the health and sustainability of ecosystems worldwide.